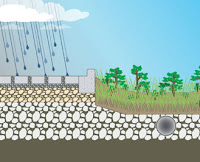
water thta doesn't soak into the ground or evaporate but instead flows across Earth's surface.
Channel
water moving down the same path create a groove.
occurs when water that is flowing as sheet picks up and carries away sediments.
Drainage basin
is the area of land from which a stream or river collects runoff.
meander
the curve grows and become a broad arc.
Ground water
water that soaks into the ground collects in these pores and empty spaces and becomes part.
Permeable
describes soil and rock with connecting pores through which water can flow.
Impermeable
water cannot pass through them.
Aquifer
a layer of permeable rock that lets water move more freely.
Water table
the upper surface of this zone.
Spring: forms when the water table meets Earth's surface; ofteb found on hillsides and used as a freshwater source.
Geyser: hot spring that erupts periodically and shoots water and steam into the air.
Cave: underground opening that can form when acidic groundwater dissoleves limestone.
Longshore current: water that run parallel to the shoreline.
Beach: deposits of sediments that are parallel to the shore.